Microsoft Cloud for Sovereignty - Part 6 - Confidential VM
Sovereign cloud series - Microsoft Cloud for Sovereignty - Part 6
This blog will give you an overview about Azure confidential VMs, one of the offerings of Azure Confidential Computing (ACC). This information can be found at Microsoft Learn.
What are Azure confidential VMs
Confidential VMs are an IaaS solution for tenants with high security and confidentiality requirements. Confidential VMs offer:
- Encryption for "data in use”, including the processor state and the virtual machine’s memory. The keys are generated by the processor and never leave it;
- Host attestation helps you verify the full health and compliance of the server before data processing begins;
- Hardware Security Module (HSM) can be attached to guard the keys of confidential VM disks, which the tenant exclusively owns;
- New UEFI boot architecture supporting the guest OS for enhanced security settings and capabilities;
- A dedicated virtual Trusted Platform Module (TPM) certifies the health of the VM, provides hardened key management, and supports use cases such as BitLocker.
In this video, Microsoft explains in visuals what Confidential VMs brings you. It gives protection against root kits, the Azure services, the Azure hypervisor and Datacenter Admins. Confidential VMs are the easiest way to migrate traditional applications, because teh complete VM will be encrypted.
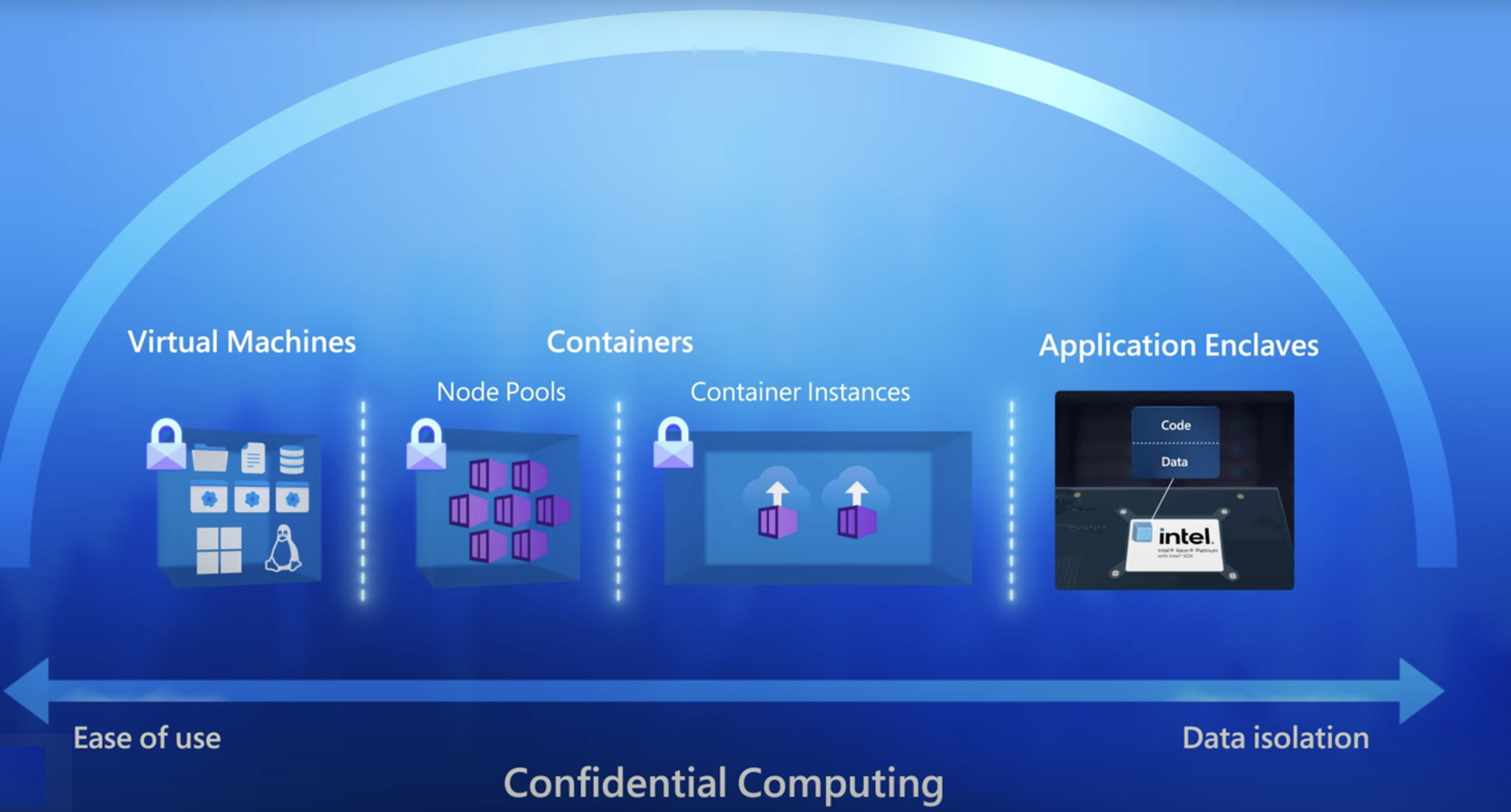
Why use Confidential VMs
- Confidential VMs address customer concerns about moving sensitive workloads off-premise into the cloud. Confidential VMs provide elevated protections for customer data from the underlying infrastructure and cloud operators. Unlike other approaches and solutions, you don't have to adapt your existing workloads to fit the platform's technical needs;
- Robust hardware-based isolation between virtual machines, hypervisor, and host management code;
- Customizable attestation policies to ensure the host's compliance before deployment;
- Cloud-based Confidential OS disk encryption before the first boot;
- VM encryption keys that the platform or the customer (optionally) owns and manages;
- Secure key release with cryptographic binding between the platform's successful attestation and the VM's encryption keys;
- Dedicated virtual Trusted Platform Module (TPM) instance for attestation and protection of keys and secrets in the virtual machine;
- Secure boot capability similar to Trusted launch for Azure VMs.
Deepdive into Confidential VMs
If you are interested in more deepdive into Confidential VMs, click the following links for more information:
- Confidential OS disk encryption - which protects all critical partitions of the disk. It also binds disk encryption keys to the virtual machine's TPM and makes the protected disk content accessible only to the VM;
- Supported VM sizes - which can chosen;
- Attestation and TPM - which explains that Confidential VMs boot only after successful attestation of the platform's critical components and security settings;
- Azure confidential virtual machines FAQ;
- Virtual TPMs in Azure confidential VMs explained;
- How to rotate customer-managed keys for confidential VMs;
- How to create an own custom image for Azure Confidential VMs.
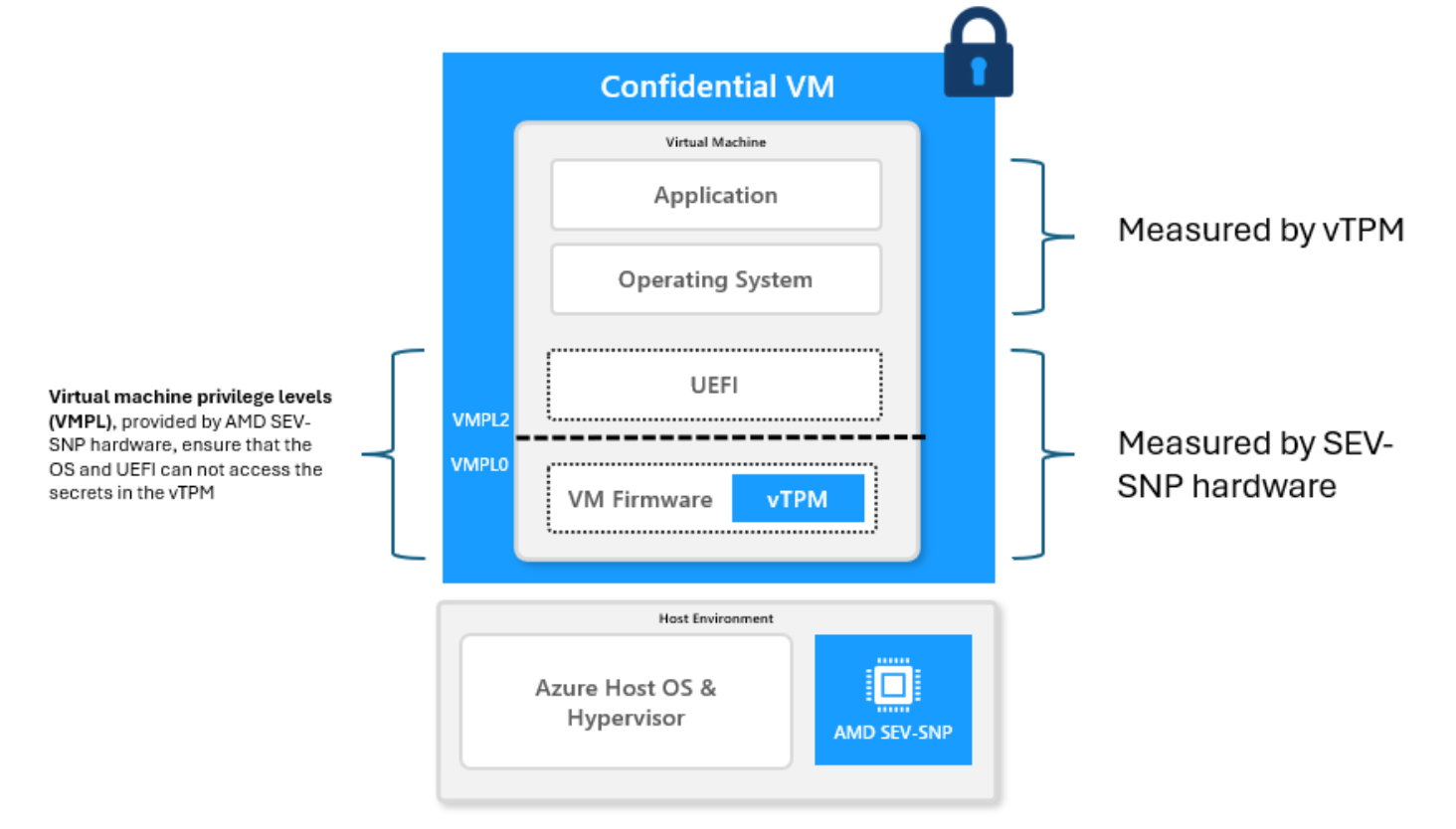
How to deploy Confidential VMs
Deployment can be done via AzureCLI, PowerShell, bicep or via ARM. For more information, click here to reach the Microsoft Learn documentation, to investigate the deployment considerations. You could also use the Confidential Virtual Machine Accelerator which can be found at this GitHub Repository. Integration with Microsoft Defender for Cloud is possible and can be found here.
You can also use the Azure Portal. Which steps you must take, are written below (with the knowledge that there is an existing Azure Key Vault Managed HSM):
- Create a "Disk Encryption Set";
- Create a "User assigned Managed Identity" and associate it with the created "Disk Encryption Set";
- In the HSM create an "RSA Key" that fit your organization policy needs;
- Assign the created "User Assigned Managed Identity the permission "Managed HSM Crypto Service Encryption User";
- Create the Confidential VM and keep in mind the following steps;
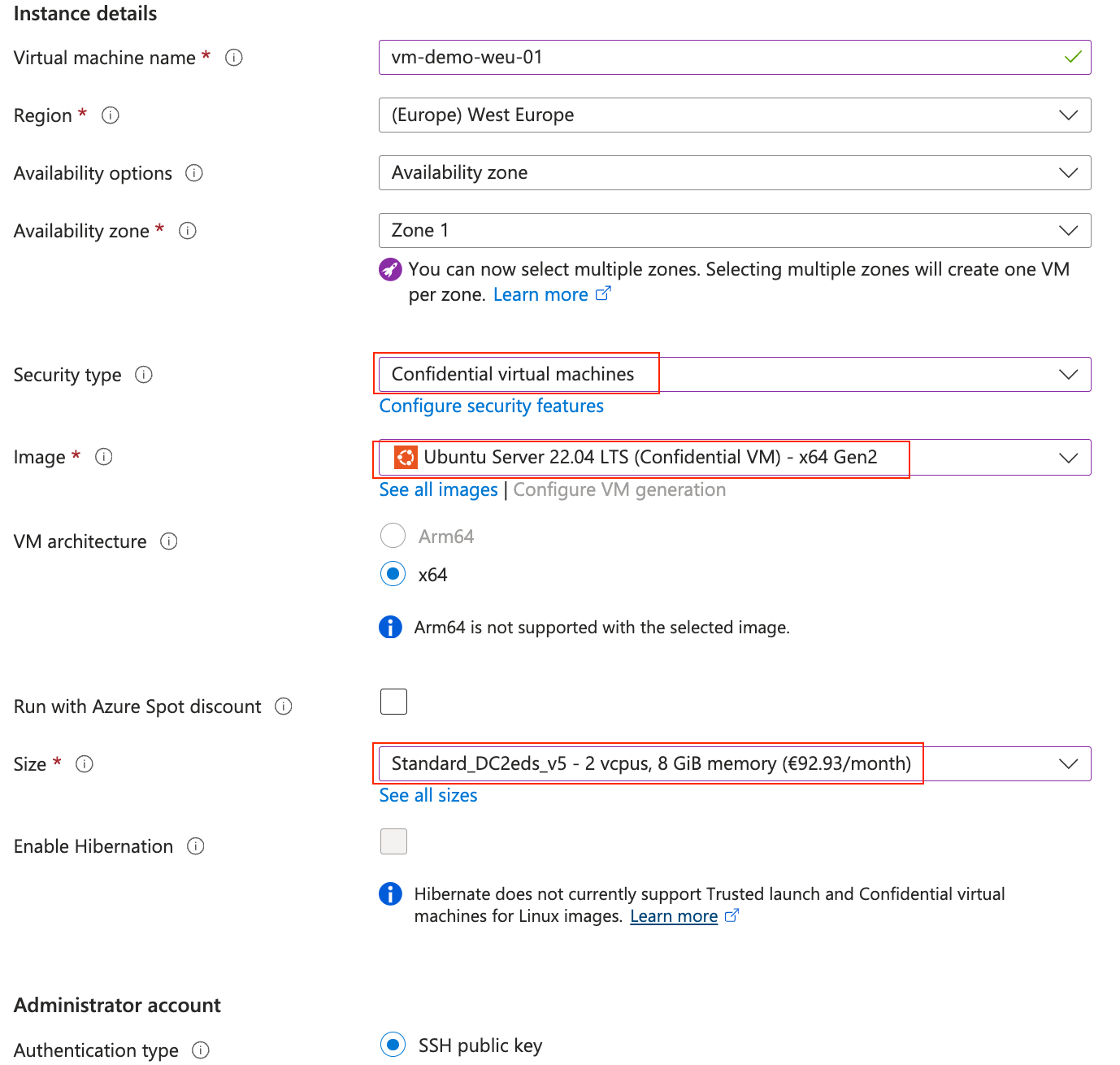
- On the "Basics" tab:
- Select by "Security type" Confidential virtual machines
- Select by "image", "Security Type" Confidential
- Select by "size", an supported vmsize
- Select by "Security type" Confidential virtual machines
- On the "Disks" tab Confidential
- Enable "Encryption at host"
- Enable "Confidential OS disk encryption" (If the your organization Sovereign policies allow it)
- "Key Management" Customer-managed key or Platform-managed and customer-managed keys
- Select the created "Disk Encryption Set"
- Enable "Encryption at host"
- Fill in the other tabs confirm the business requirements and Press "Review + Create".
- On the "Basics" tab:
Limitations to take into consideration
The following limitations currently exists for confidential VMs:
- VM SKU sizes;
- OS support;
- Regional Support;
- Feature Support;
- Azure Backup support for confidential VMs using Customer Managed Keys which is currently in private preview;
- High availability and disaster recovery is the customers responsibility;
- Confidential Temp Disk Encryption for Confidential VMs is currently in Public Preview;
- Encryption to an extra Data disks is currently not supported.
- Automatic rotating of Customer Managed Keys in combination with Azure Key Vault Managed HSM is currently not supported. This proces is manual by first shutdown the VM and then replace the HSM key.